This post is also available in:
Français
DNS or the Domain Name System is the the backbone of the modern internet as we know it
When you enter a website’s URL into your browser’s address bar, like “www.example.com,” you expect to be taken to the corresponding website. But, have you ever wondered how this process works seamlessly behind the scenes? The answer lies in DNS, or Domain Name System.
What is DNS?
DNS, short for Domain Name System, is like the internet’s phonebook. It’s a fundamental component of the web that translates human-friendly domain names, such as “www.example.com,” into IP addresses, like “192.168.1.1.” This translation is crucial because computers communicate with each other using IP addresses, not domain names. DNS ensures that when you type a URL, your request reaches the correct destination.
How Does DNS Work?
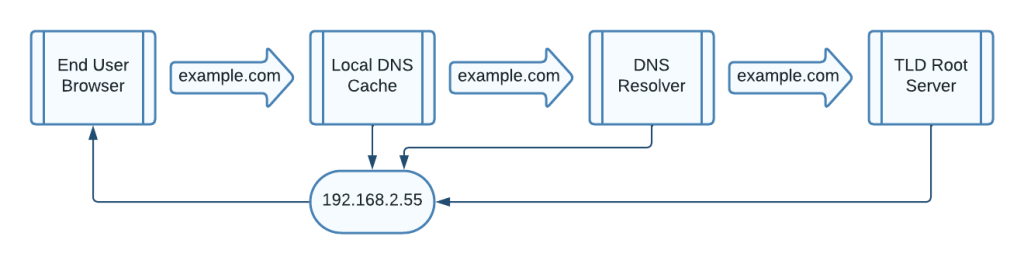
Here’s a simplified breakdown of how DNS functions:
- Request Initiation: When you enter a URL, your computer first checks its local DNS cache to see if it already knows the corresponding IP address. If not, it sends a request to a DNS resolver.
- Contacting a DNS Resolver: The DNS resolver is like a middleman between your device and the internet. It maintains a vast database of domain names and their corresponding IP addresses. It tries to find the IP address for the requested domain in its cache. If it doesn’t have it, it forwards the request to a DNS root server.
- Root Server Lookup: The root server doesn’t have the specific IP address but can direct the resolver to the authoritative DNS server responsible for the top-level domain (TLD), like “.com” or “.org.”
- TLD Server: The TLD server, which manages domains ending with a specific extension, points the resolver to the authoritative DNS server for the exact domain you’re seeking.
- Authoritative DNS Server: Finally, the authoritative DNS server has the precise IP address for the requested domain. It sends this information back to the resolver.
- Response to Your Device: The resolver now knows the IP address and sends it to your device. Your computer caches this information to speed up future requests to the same domain.
What Does DNS Do for Your Domain?
DNS plays a vital role in ensuring your online presence:
- Accessibility: It enables users to access your website by typing your domain name instead of remembering numerical IP addresses.
- Redundancy: DNS offers redundancy by distributing your website’s IP address across multiple servers, ensuring reliability and availability.
- Load Balancing: It can distribute traffic evenly across multiple servers, optimizing performance and preventing server overload.
- Email Delivery: DNS settings also control email delivery, ensuring that emails sent to your domain reach the correct mail servers.
In summary, DNS is an unsung hero of the internet, quietly working behind the scenes to make sure you can effortlessly visit your favorite websites. It transforms human-readable domain names into machine-readable IP addresses, making the internet user-friendly and accessible to everyone.
So next time you type a web address, remember that DNS is hard at work, ensuring your online journey is smooth and hassle-free.
How can I update my DNS?
You can find out how to update your DNS in this article.
Still need help?
If you are in need of assistance, you can contact our support staff using one of the following methods:
Send us an email – 24/7/365
- Technical Support
- Billing Issues
- Sales Inquires
Live Chat – 24/7/362
Access our Live Chat support team from your Easyhosting Portal
Phone Support – Monday to Friday, 9:00am to 7:00pm EST
Call one of our Phone Support team members anytime between 9:00am and 7:00pm, eastern time at 1-888-390-1210.
